Separate aircraft by providing a time or distance interval between aircraft consistent with the required minima. Longitudinal separation expressed in distance may be applied as prescribed in Chapter 6.
NOTE -
Longitudinal separation minima is contained in:
Section 7, North Atlantic ICAO Region.
Section 8, Caribbean ICAO Region.
Section 9, Pacific ICAO Region.
Section 10, North American ICAO Region.
Separate aircraft longitudinally in accordance with the following:
 |
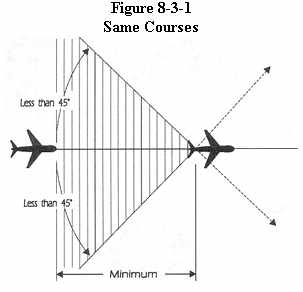
a. Same courses: Ensure that the spacing between aircraft is not
less than the applicable minimum required. (See Figure 8-3-1)
b. Crossing courses: Ensure that the spacing at the point of
intersection is not less than the applicable minimum required. (See Figure
8-3-2)
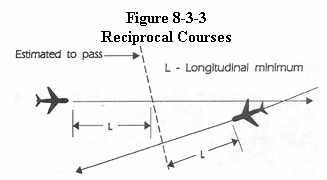
c. Reciprocal courses:
1. Ensure that aircraft are vertically separated for a time
interval equal to the applicable minimum required before and after the
aircraft are estimated to pass. (See Figure 8-3-3)
 |
 |
2. Vertical separation may be discontinued after one of the following
conditions are met:
 |
(a) Both aircraft have reported passing a significant point
and the aircraft are separated by at least the applicable minimum required
for the same direction longitudinal spacing; (See Figure 8-3-4) or
(b) Both aircraft have reported passing ground based NAVAIDs
or DME fixes indicating that they have passed each other.
The following conditions shall be met when the Mach number technique
is being applied:
a. Aircraft Types: Turbojet aircraft only.
b. Routes:
1. The aircraft follow the same track or continuously diverging
tracks, and
2. The aircraft concerned have reported over a common point;
or
3. If the aircraft have NOT reported over a common point, either
radar or other approved means are used to ensure that the appropriate time
interval will exist at the common point; or
4. If a common point does not exist, either radar or other approved
means are used to verify that the appropriate time interval will exist
at a significant point on each track from which the tracks continuously
diverge.
c. Altitudes:
1. Assign only a single cardinal altitude to each aircraft.
2. The aircraft concerned are in level, climbing or descending
flight.
d. Mach Number Assignment:
1. A Mach number (or, when appropriate, a range of Mach numbers)
shall be issued to each aircraft.
NOTE -
1 - ICAO DOC 7030/4 requires pilots to strictly adhere to the last
assigned Mach number (or range of Mach numbers), even during climbs and
descents, unless revised by ATC.
2 - When it is necessary to issue crossing restrictions to ensure the
appropriate time interval it may be impossible for an aircraft to comply
with both the clearance to meet the crossing restrictions and the clearance
to maintain a single, specific Mach number.
REFERENCE -
ICAO DOC 9426-AN/924, Part II, section 2, paragraph 2.3.4, 2.4.7, and
2.5.3.
EXAMPLE -
"Maintain Mach point eight four or greater."
"Maintain Mach point eight three or less."
"Maintain Mach point eight two or greater; do not exceed Mach point
eight four."
e. Separation Criteria:
1. The use of Mach number technique allows for the application
of reduced longitudinal separation minima. However, the prescribed longitudinal
separation between successive aircraft flying at the same level shall be
provided over the entry point and on a particular track or tracks, or exist
when climb or descent to the level of another aircraft is accomplished
into the area concerned.
2. The applicable longitudinal separation minima is maintained
by:
(a) Ensuring that the spacing between the estimated positions
of the aircraft is not less than the prescribed minimum.
(b) Continuously monitoring aircraft position reports
and updating control estimates along the aircraft's track(s). If after
establishing the Mach number technique between aircraft, control information
indicates that less than the applicable minima between aircraft may exist,
immediately:
(1) Issue crossing restrictions to ensure the appropriate
longitudinal minima at the next significant point, or
(2) Assign revised Mach numbers appropriate for
the estimated interval, or
(3) Establish vertical separation.
NOTE -
Control estimates are calculated by the controller using known wind
patterns, previous aircraft transit times, pilot progress reports, and
pilot estimates.
f. Relative Speeds:
1. The lead aircraft maintains the same or a greater Mach number
than the following aircraft; or
2. If the following aircraft is faster than the lead aircraft,
ensure that the appropriate time interval will exist until another form
of separation is achieved.
NOTE -
A "rule of thumb" may be applied which allows clearances to be issued
in a timely manner, provided the expected minimum longitudinal separation
over the exit point is subsequently confirmed when the calculated flight
progress strip data becomes available. This rule of thumb can be stated
as follows: for each 600 NM in distance between the entry and exit points
of the area where the Mach number technique is used, add 1 minute for each
0.01 difference in Mach number for the two aircraft concerned to compensate
for the fact that the second aircraft is overtaking the first aircraft.
(See Table 8-3-1.)
Table 8-3-1
Application of the Mach number technique
when the following aircraft is faster.
-----------------------------------------------------------------
Key:
Difference in MACH
Distance to Fly and
Separation (in Minutes) Required at Entry Point
-----------------------------------------------------------------
Difference in MACH = 0.01
1 - 600
NM : 11
601 - 1200 NM : 12
1201 - 1800 NM : 13
1801 - 2400 NM : 14
2401 - 3000 NM : 15
-----------------------------------------------------------------
Difference in MACH = 0.02
1 - 600 NM :
12
601 - 1200 NM : 14
1201 - 1800 NM : 16
1801 - 2400 NM : 18
2401 - 3000 NM : 20
-----------------------------------------------------------------
Difference in MACH = 0.03
1 - 600 NM :
13
601 - 1200 NM : 16
1201 - 1800 NM : 19
1801 - 2400 NM : 22
2401 - 3000 NM : 25
-----------------------------------------------------------------
Difference in MACH = 0.04
1 - 600 NM :
14
601 - 1200 NM : 18
1201 - 1800 NM : 22
1801 - 2400 NM : 26
2401 - 3000 NM : 30
-----------------------------------------------------------------
Difference in MACH = 0.05
1 - 600 NM :
15
601 - 1200 NM : 20
1201 - 1800 NM : 25
1801 - 2400 NM : 30
2401 - 3000 NM : 35
-----------------------------------------------------------------
Difference in MACH = 0.06
1 - 600 NM :
16
601 - 1200 NM : 22
1201 - 1800 NM : 28
1801 - 2400 NM : 34
2401 - 3000 NM : 40
-----------------------------------------------------------------
Difference in MACH = 0.07
1 - 600 NM :
17
601 - 1200 NM : 24
1201 - 1800 NM : 31
1801 - 2400 NM : 38
2401 - 3000 NM : 45
-----------------------------------------------------------------
Difference in MACH = 0.08
1 - 600 NM :
18
601 - 1200 NM : 26
1201 - 1800 NM : 34
1801 - 2400 NM : 42
2401 - 3000 NM : 50
-----------------------------------------------------------------
Difference in MACH = 0.09
1 - 600 NM :
19
601 - 1200 NM : 28
1201 - 1800 NM : 37
1801 - 2400 NM : 46
2401 - 3000 NM : 55
-----------------------------------------------------------------
Difference in MACH = 0.10
1 - 600 NM :
20
601 - 1200 NM : 30
1201 - 1800 NM : 40
1801 - 2400 NM : 50
2401 - 3000 NM : 60
-----------------------------------------------------------------