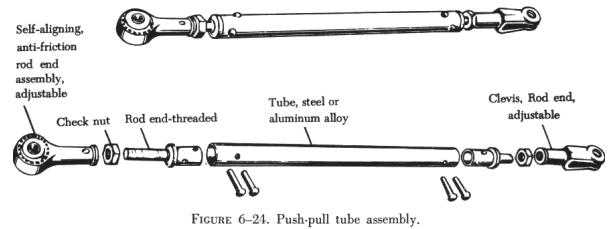
Push-pull tubes are used as linkage in various types of mechanically operated systems. This type linkage eliminates the problem of varying tension and permits the transfer of either compression or tension stress through a single tube.
A push-pull tube assembly consists of a hollow aluminum alloy or steel tube with an adjustable end fitting and a checknut at either end. (See figure 6-24.) The checknuts secure the end fittings after the tube assembly has been adjusted to its correct length. Push-pull tubes are generally made in short lengths to prevent vibration and bending under compression loads.

The three main types of pins used in aircraft structures are the taper pin, flathead pin, and cotter pin. Pins are used in shear applications and for safetying. Roll pins are finding increasing uses in aircraft construction.
Taper Pins
Plain and threaded taper pins (AN385 and AN386) are used in joints which carry shear loads and where absence of play is essential. The plain taper pin is drilled and usually safetied with wire. The threaded taper pin is used with a taper pin washer (AN975) and shear nut (safetied with cotter pin) or selflocking nut.
Flathead Pin
Commonly called a clevis pin, the flathead pin (MS20392) is used with tierod terminals and in secondary controls which are not subject to continuous operation. The pin is customarily installed with the head up so that if the cotter pin fails or works out, the pin will remain in place.
Cotter Pins
The AN380 cadmium plated, low carbon steel cotter pin is used for safetying bolts, screws, nuts, other pins, and in various applications where such safetying is necessary. The AN381 corrosion resistant steel cotter pin is used in locations where nonmagnetic material is required, or in locations where resistance to corrosion is desired.
Rollpins
The rollpin is a pressed fit pin with chamfered ends. It is tubular in shape and is slotted the full length of the tube. The pin is inserted with hand tools and is compressed as it is driven into place. Pressure exerted by the roll pin against the hole walls keeps it in place, until deliberately removed with a drift punch or pin punch.