
This chapter introduces the various classifications
of airspace and provides information on the requirements
to operate in such airspace. For further information,
consult the Pilot’s Handbook of Aeronautical
Information, the Aeronautical Information Manual
(AIM) and Title 14 of the Code of Federal Regulations
(14 CFR) parts 71, 73, and 91.
Powered parachutes (PPC) share the airspace with
all other types of aircraft and must avoid the flow
of fixed wing aircraft. Although most PPCs fly low,
slow and close to the field, you must be aware of the
airspace in which you are operating. Each type of airspace
has communication, equipment, visibility and
cloud clearance requirements, and therefore may require
additional pilot training with logbook endorsements.
Some airspace may not be accessible (Class A)
while other airspace (Class B and Class C) may not
be prudent for PPC operation. Knowing the types of
airspace and their requirements is necessary for safe
and proper PPC operations.
The two categories of airspace are: regulatory and
non-regulatory. Within these two categories, there are
four types: controlled, uncontrolled, special use, and
other airspace.
Each type of airspace may have different minimum
pilot certification, equipment, visibility and cloud
clearance, and entry requirements.
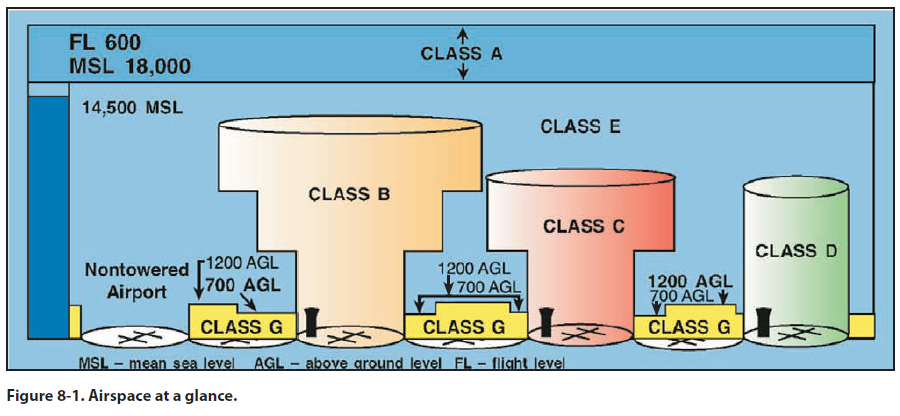
Figure 8-1 presents a profile view of the dimensions
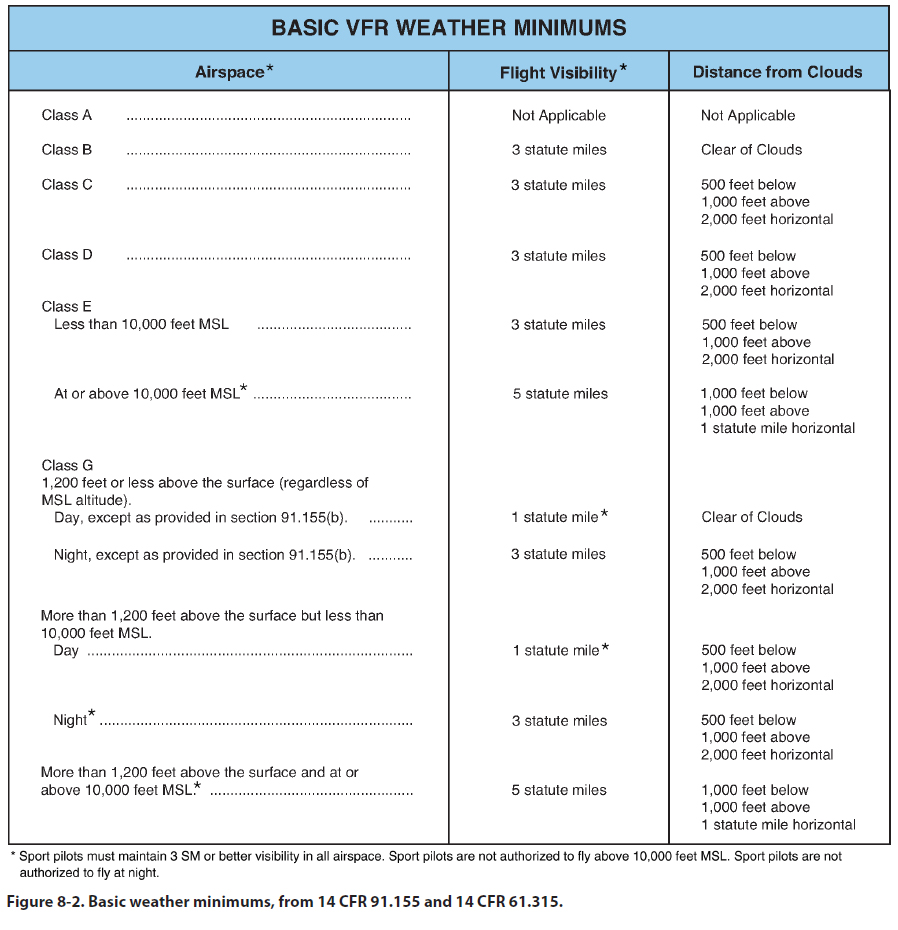
of various airspace classes. Figure 8-2 provides the
basic weather minimums for operating in the different
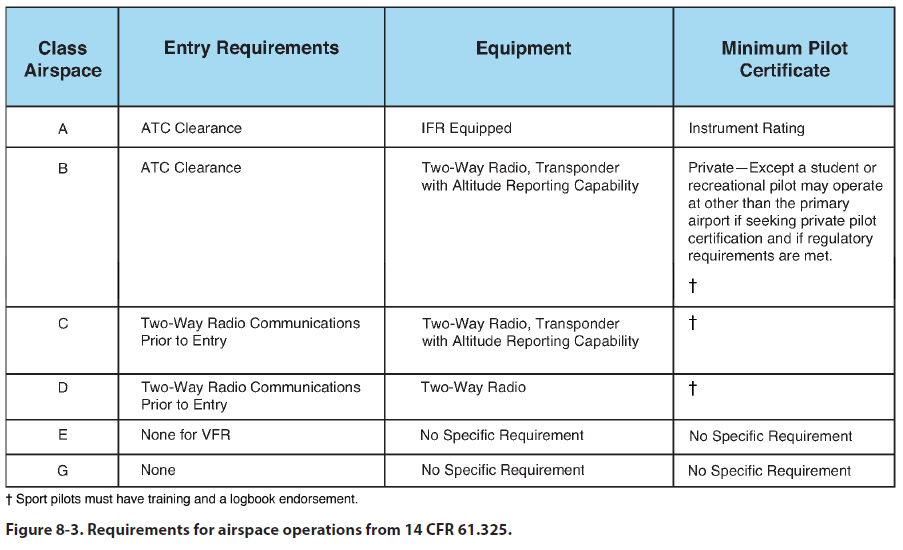
airspace classes. Figure 8-3 lists the operational and
equipment requirements. Refer to these figures as you
review this chapter.
Controlled Airspace
Controlled airspace is a generic term that covers the
different classifications of airspace and defined dimensions
within which air traffic control service is
provided in accordance with the airspace classification.
Controlled airspace consists of Class A, Class B,
Class C, Class D, and Class E.
Class A Airspace
Class A airspace is generally the airspace from 18,000
feet mean sea level (MSL) up to and including 60,000
feet (FL600), including the airspace overlying the waters within 12 nautical miles (NM) of the coast of
the 48 contiguous states and Alaska. Unless otherwise
authorized, all operation in Class A airspace will be
conducted under instrument flight rules (IFR). It is not
likely PPCs will be operated in Class A airspace.
|

