|
MAXIMUM AUTHORIZED ALTITUDE
A maximum authorized altitude (MAA) is a published
altitude representing the maximum usable altitude or
flight level for an airspace structure or route segment. It
is the highest altitude on a Federal airway, jet route,
RNAV low or high route, or other direct route for which
an MEA is designated at which adequate reception of
navigation signals is assured. MAAs represent procedural
limits determined by technical limitations or other
factors such as limited airspace or frequency interference
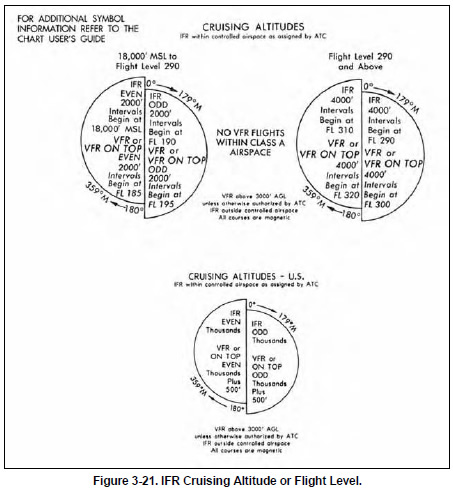
of ground based facilities. IFR CRUISING ALTITUDE OR FLIGHT LEVEL
In controlled airspace, pilots must maintain the altitude
or flight level assigned by ATC, although if the ATC
clearance assigns “VFR conditions on-top,” an altitude
or flight level as prescribed by Part 91.159 must be
maintained. In uncontrolled airspace (except while in a
holding pattern of 2 minutes or less or while turning) if
operating an aircraft under IFR in level cruising flight,
an appropriate altitude as depicted in the legend of
NACO IFR en route high and low altitude charts must
be maintained. [Figure 3-21]
When operating on an IFR flight plan below 18,000 feet
MSL in accordance with a VFR-on-top clearance, any
VFR cruising altitude appropriate to the direction of
flight between the MEA and 18,000 feet MSL may be
selected that allows the flight to remain in VFR conditions.
Any change in altitude must be
reported to ATC and pilots must comply
with all other IFR reporting procedures.
VFR-on-top is not authorized in Class A
airspace. When cruising below 18,000
feet MSL, the altimeter must be adjusted
to the current setting, as reported by a
station within 100 NM of your position.
In areas where weather-reporting stations
are more than 100 NM from the
route, the altimeter setting of a station
that is closest may be used. During IFR
flight, ATC advises flights periodically
of the current altimeter setting, but it
remains the responsibility of the pilot or
flight crew to update altimeter settings
in a timely manner. Altimeter settings
and weather information are available
from weather reporting facilities operated
or approved by the U.S. National
Weather Service, or a source approved
by the FAA. Some commercial operators
have the authority to act as a
government-approved source of
weather information, including
altimeter settings, through certification
under the FAA’s Enhanced
Weather Information System.
Flight level operations at or above 18,000 feet MSL
require the altimeter to be set to 29.92. A flight level
(FL) is defined as a level of constant atmospheric pressure
related to a reference datum of 29.92 in. Hg. Each
flight level is stated in three digits that represent hundreds
of feet. For example, FL 250 represents an
altimeter indication of 25,000 feet. Conflicts with
traffic operating below 18,000 feet MSL may arise
when actual altimeter settings along the route of flight
are lower than 29.92. Therefore, Part 91.121 specifies
the lowest usable flight levels for a given altimeter
setting range.
LOWEST USABLE FLIGHT LEVEL
When the barometric pressure is 31.00 inches of mercury
or less and pilots are flying below 18,000 feet
MSL, use the current reported altimeter setting. This is
important because the true altitude of an aircraft is
lower than indicated when sea level pressure is lower
than standard. When an aircraft is en route on an instrument
flight plan, air traffic controllers furnish this
information at least once while the aircraft is in the controller’s
area of jurisdiction. According to Part 91.144,
when the barometric pressure exceeds 31.00 inches
Hg., the following procedures are placed in effect by
NOTAM defining the geographic area affected: Set
31.00 inches for en route operations below 18,000 feet
MSL and maintain this setting until beyond the affected
area. Air traffic control issues actual altimeter settings and advises pilots to set 31.00 inches in their altimeter,
for en route operations below 18,000 feet MSL in
affected areas. If an aircraft has the capability of setting
the current altimeter setting and operating into airports
with the capability of measuring the current altimeter
setting, no additional restrictions apply. At or above
18,000 feet MSL, altimeters should be set to 29.92
inches of mercury (standard setting). Additional procedures
exist beyond the en route phase of flight.
The lowest usable flight level is determined by the
atmospheric pressure in the area of operation. As local
altimeter settings fall below 29.92, pilots operating in
Class A airspace must cruise at progressively higher
indicated altitudes to ensure separation from aircraft
operating in the low altitude structure as follows:
Current Altimeter Setting Lowest Usable Flight Level
- 29.92 or higher 180
- 29.91 to 29.42 185
- 29.41 to 28.92 190
- 28.91 to 28.42 195
- 28.41 to 27.92 200
When the minimum altitude, as prescribed in Parts
91.159 and 91.177, is above 18,000 feet MSL, the lowest
usable flight level is the flight level equivalent of
the minimum altitude plus the number of feet specified
according to the lowest flight level correction factor as
follows:
Altimeter Setting Correction Factor
- 29.92 or higher none
- 29.91 to 29.42 500 Feet
- 29.41 to 28.92 1000 Feet
- 28.91 to 28.42 1500 Feet
- 28.41 to 27.92 2000 Feet
- 27.91 to 27.42 2500 Feet
|
