|
|
| INSTRUMENT PROCEDURES HANDBOOK |
|
REQUIRED NAVIGATION PERFORMANCE As RNAV systems grow in
sophistication, high technology
FMS and GPS avionics are
gaining popularity as NDBs,
VORs, and LORAN are being
phased out. As a result, new procedures
are being introduced,
including RNP, RVSM, and
minimum navigation performance
specifications (MNPS).
ICAO defines an RNP “X” specification
as requiring on-board
performance monitoring and
alerting. Even such terms as
gross navigation errors
(GNEs) are being introduced
into the navigation equation. If
you commit a GNE in the
North Atlantic oceanic region
of more than 25 NM laterally
or 300 feet vertically, it has a
detrimental effect on the overall
targeted level of safety of
the ATC airspace system in
this region. This applies to
commercial operators, as well
as Part 91 operators, all of
whom must be knowledgeable
on procedures for operations
in North Atlantic airspace,
contained in the North Atlantic
MNPS Operations Manual.
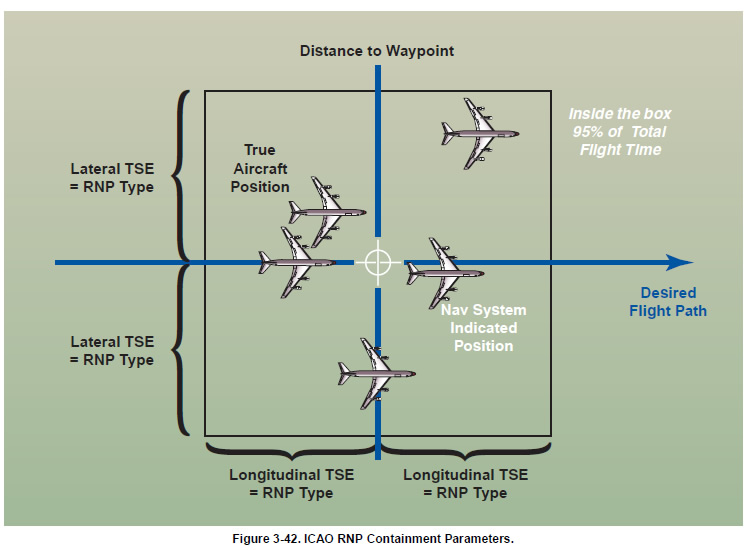
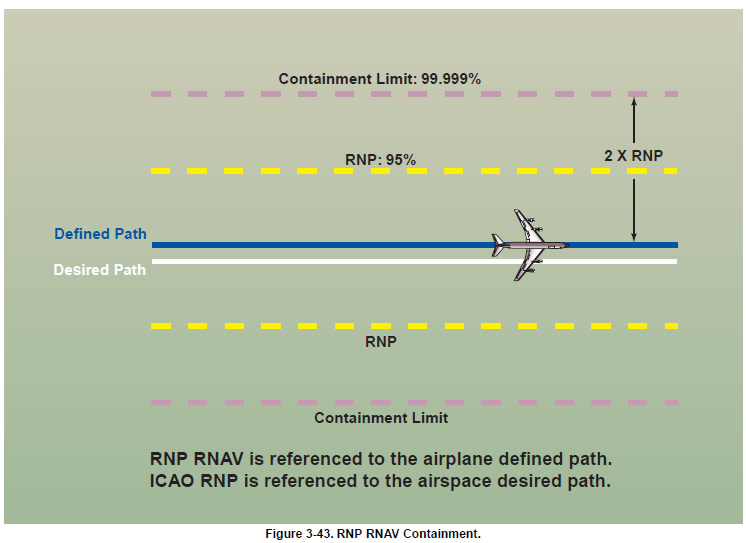
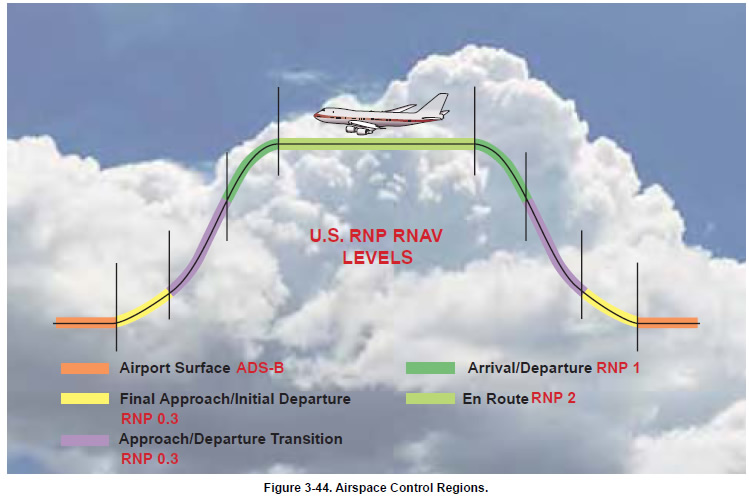
RNP RNAV is an industry-expanded specification beyond ICAO-defined RNP. Some of the benefits of RNP RNAV includes being an aid in both separation and collision risk assessment. RNP RNAV can further reduce route separation. Figure 3-43 depicts route separation, that can now be reduced to four times the RNP value, which further increases route capacity within the same airspace. The containment limit quantifies the navigation performance where the probability of an unannunciated deviation greater than 2 x RNP is less than 1 x 10-5. This means that the pilot will be alerted when the TSE can be greater than the containment limit. Figure 3-44 shows the U.S. RNP RNAV levels by airspace control regions, including RNP 2 for the en route phase of flight, and Figure 3-45 on page 3-40 illustrates the U.S. standard RNP (95%) levels.
|