|
|
| INSTRUMENT PROCEDURES HANDBOOK |
|
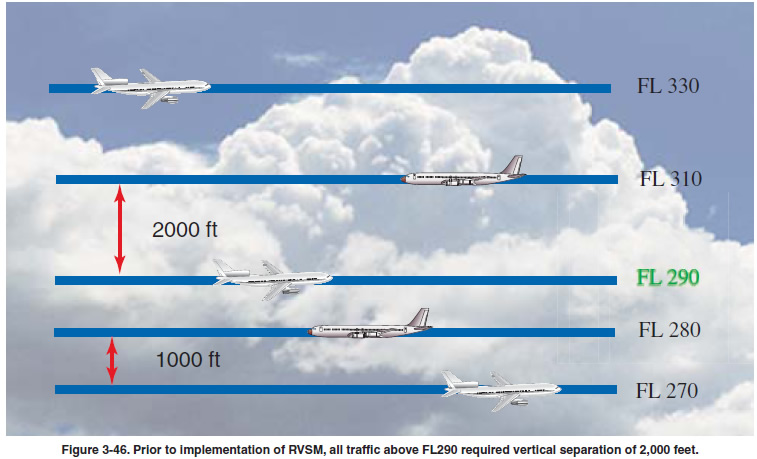
REDUCED VERTICAL SEPARATION MINIMUMS In 1960, the minimum vertical separation between airplanes
above FL 290 was officially increased to 2,000 feet. This
was necessary because of the relatively large errors in barometric
altimeters at high altitudes. Since that time, increased
air traffic worldwide has begun to approach (and sometimes
exceed) the capacity of the most popular high-altitude
routes. Likewise, very accurate altitude determination by
satellite positioning systems makes it possible to change the
minimum vertical separation for properly equipped airplanes
back to the pre-1960 standard of 1,000 feet. [Figure
3-46 on page 3-41] RVSM airspace is any airspace between
FL 290 and FL 410 inclusive,where airplanes are separated
by 1,000 feet vertically. In the early 1980ís, programs
were established to study the concept of reduced vertical
separation minimums (RVSM). RVSM was found
to be technically feasible without imposing unreasonable
requirements on equipment. RVSM is the most
effective way to increase airspace capacity to cope with
traffic growth. Most of the preferred international and
domestic flight routes are under both RVSM and RNP
RNAV rules.
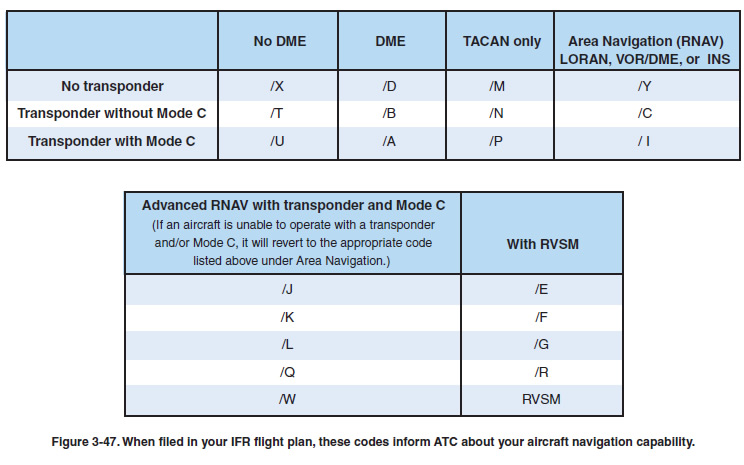
Using the appropriate suffix in Block 3 on the IFR flight plan lets ATC know that your flight conforms to the necessary standards and is capable of using RNP routes or flying in RVSM airspace. The equipment codes changed significantly in 2005 and are shown in Figure 3-47.
|