|
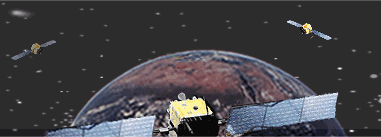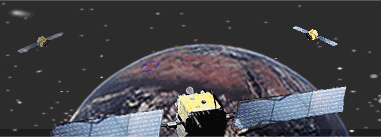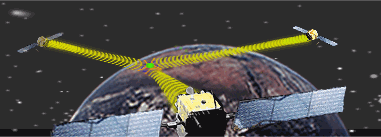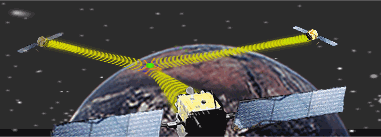
The technology
behind GPS is relatively simple. Each of the 24 satellites, orbiting 11,000
miles above the surface of the earth, emits signals to receivers below.
By measuring the travel time of a signal transmitted from each satellite,
a receiver can calculate its distance from that satellite. Satellite positions
are used by a receiver as precise reference points to determine the location
of a receiver. When receiving the signals from at least 4 satellites, a
receiver can determine latitude, longitude, altitude, and time. The basic
GPS service provides users with approximately 100 meter accuracy 95% of
the time anywhere on or near the surface of the earth. |
|
 |

